Click here and press the right key for the next slide.
(This may not work on mobile or ipad. You can try using chrome or firefox, but even that may fail. Sorry.)
also ...
Press the left key to go backwards (or swipe right)
Press n to toggle whether notes are shown (or add '?notes' to the url before the #)
Press m or double tap to slide thumbnails (menu)
Press ? at any time to show the keyboard shortcuts

The Argument and Some Objections
[email protected]
the argument
1. ‘Moral convictions and the emotions they evoke shape political attitudes’
2. There are at least two fundamental domains of human morality, including harm and purity.
3. ‘liberals and conservatives possess different moral profiles’
4. ‘liberals express greater levels of environmental concern than do conservatives in part because liberals are more likely to view environmental issues in moral terms.’
5. ‘exposing conservatives to proenvironmental appeals based on moral concerns that uniquely resonate with them will lead them to view the environment in moral terms and be more supportive of proenvironmental efforts.’
1. ‘Moral convictions and the emotions they evoke shape political attitudes’
2. There are at least two fundamental domains of human morality, including harm and purity.
3. ‘liberals and conservatives possess different moral profiles’
4. ‘liberals express greater levels of environmental concern than do conservatives in part because liberals are more likely to view environmental issues in moral terms.’
5. ‘exposing conservatives to proenvironmental appeals based on moral concerns that uniquely resonate with them will lead them to view the environment in moral terms and be more supportive of proenvironmental efforts.’
Do cultural differences in moral psychology explain political conflict on climate change?
objection 1
1. ‘Moral convictions and the emotions they evoke shape political attitudes’
2. There are at least two fundamental domains of human morality, including harm and purity.
3. ‘liberals and conservatives possess different moral profiles’
4. ‘liberals express greater levels of environmental concern than do conservatives in part because liberals are more likely to view environmental issues in moral terms.’
5. ‘exposing conservatives to proenvironmental appeals based on moral concerns that uniquely resonate with them will lead them to view the environment in moral terms and be more supportive of proenvironmental efforts.’
What does the Moral Foundations Questionnaire measure?
Social Intuitionist Model
Unreflective ethical judgements are primarily consequences of moral foundations plus cultural learning.
If Moral Disengagement Is Real
Unreflective ethical judgements are consequences of moral foundations, cultural learning and reasoning from known principles.
(Your answers need not reflect your culture.)
1. ‘Moral convictions and the emotions they evoke shape political attitudes’
2. There are at least two fundamental domains of human morality, including harm and purity.
3. ‘liberals and conservatives possess different moral profiles’
4. ‘liberals express greater levels of environmental concern than do conservatives in part because liberals are more likely to view environmental issues in moral terms.’
5. ‘exposing conservatives to proenvironmental appeals based on moral concerns that uniquely resonate with them will lead them to view the environment in moral terms and be more supportive of proenvironmental efforts.’
objection 2
1. ‘Moral convictions and the emotions they evoke shape political attitudes’
2. There are at least two fundamental domains of human morality, including harm and purity.
3. ‘liberals and conservatives possess different moral profiles’
4. ‘liberals express greater levels of environmental concern than do conservatives in part because liberals are more likely to view environmental issues in moral terms.’
5. ‘exposing conservatives to proenvironmental appeals based on moral concerns that uniquely resonate with them will lead them to view the environment in moral terms and be more supportive of proenvironmental efforts.’
Does Moral Foundations Theory provide a model that is invariant?
Davies et al, 2014 : metric invariance for gender groups
(scalar invariance not tested)
Davis et al, 2014 : metric but not scalar invariance for Black people vs White people
Dogruyol et al, 2019 : metric non-invariance for WEIRD/non-WEIRD samples
Iurino and Saucier, 2020 : five-factor model not supported
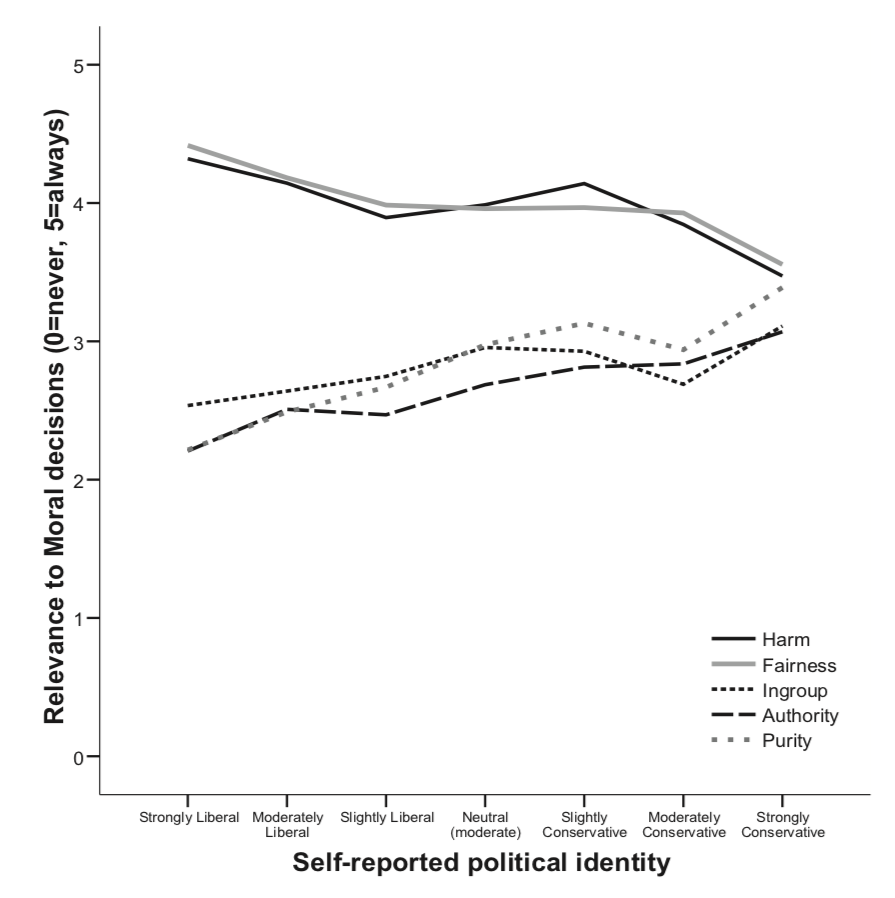
Graham et al, 2009 figure 1 p.notes.handout.show: :t
‘across subscales, there were problems with scalar invariance, which suggests that researchers may need to carefully consider whether this scale is working similarly across groups before conducting mean comparisons’ (Davis et al., 2016, p. e27)
objection 3

Graham et al, 2009 figure 1
The Joan-Lars-Joseph objection
The evidence on cultural variation says socially conservative participants tend to regard all five foundations as roughly equally morally relevant.
This does not generate the prediction that socially conservative participants will be more likely to view climate issues as ethical issues when linked on one foundation (e.g. purity) than when linked to another foundation (e.g. harm).
puzzle
Given that the evidence for cultural variation in moral psychology is at best weak,
and given that the theoretical argument for moral reframing is flawed,
why does moral reframing seem to work?